
India’s Engineering Goods sector comprises manufacturing iron, steel, related products, non-ferrous metals, industrial machinery, automobiles, auto components, and other engineering products.
Engineering Goods Includes
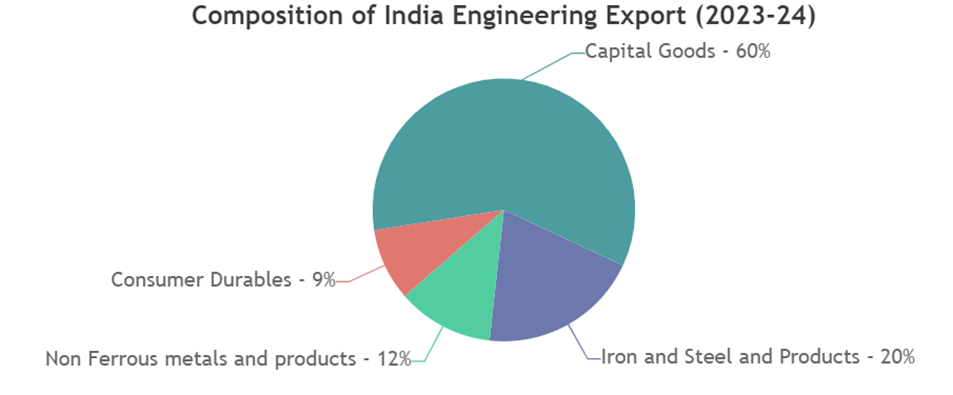
- Capital goods- About half of India’s engineering exports, including industrial machinery, electrical machinery, and auto and auto parts
- Iron, steel, and products
- Non-ferrous metals and products
- Miscellaneous items- 17.68% of India’s engineering exports, including aircraft, spacecraft, ships, boats, and floating structures
Statistical Representation of Engineering Exports
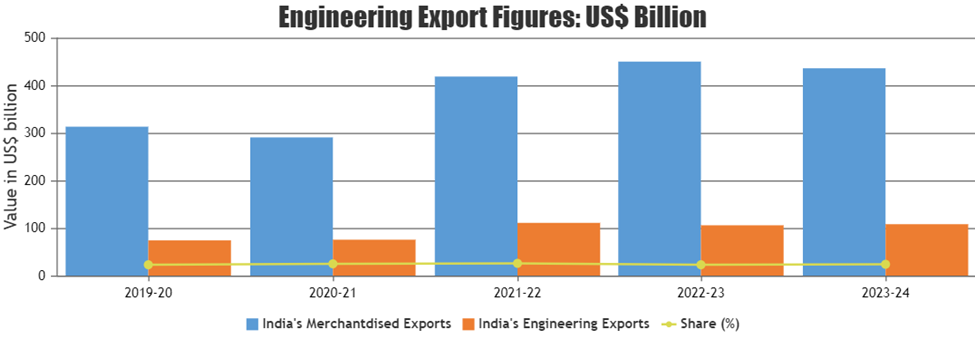
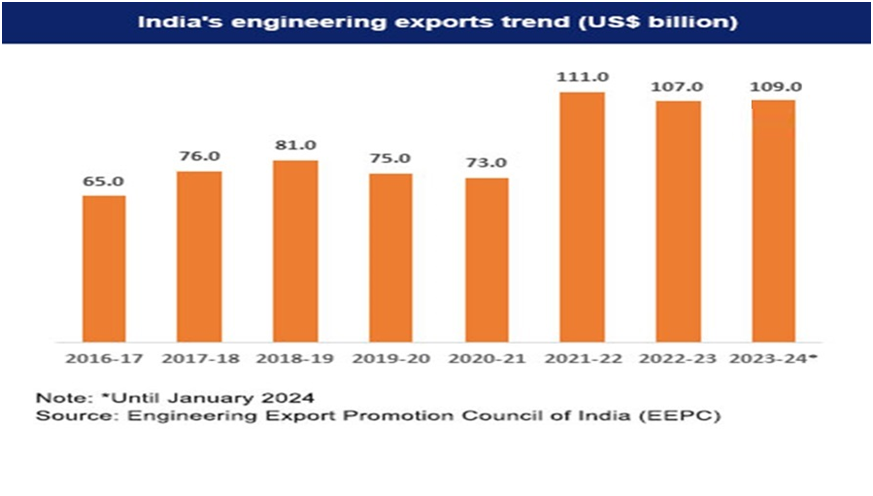
Export Trends
The engineering goods export of India had a share of 23.92% out of the total exports during the financial year 2022-23 from the country.
The impressive growth in Engineering Goods exports in recent years has largely been due to the zero-duty Export Promotion Capital Goods (EPCG) scheme of the Ministry of Commerce & Industry which forms part of the Foreign Trade Policy (FTP) of the Government of India.
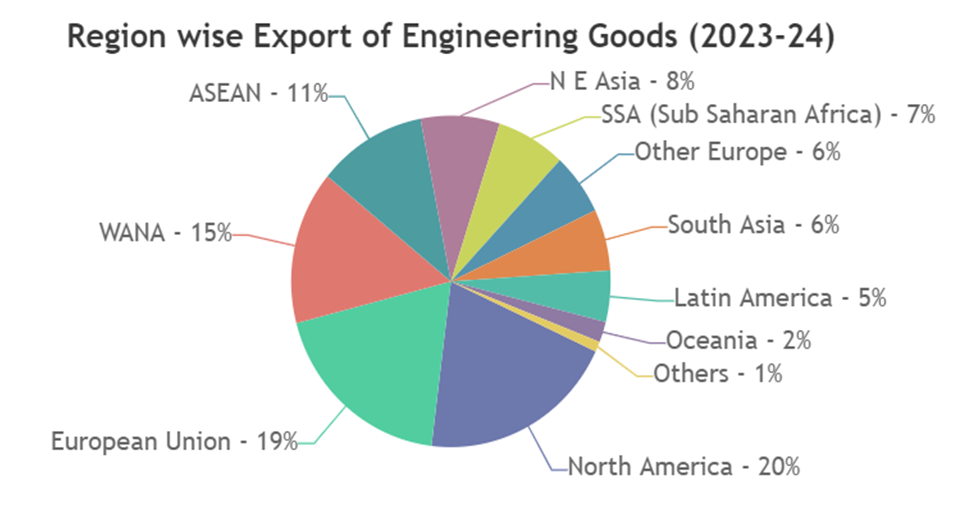
Export Destinations
- United States
- United Kingdom
- France
- Brazil
- Philippines
- Singapore
- Turkey
- Morocco
- United Arab Emirates
- Thailand
- South Africa
- Russia
Government Initiatives
- The government of India has implemented various export promotion schemes, such as the Zero Duty Export Promotion Capital Goods (EPCG) scheme, Towns of Export Excellence (TEE), Market Access Initiative (MAI), etc. These schemes are aimed at encouraging the exporter and to help increase the revenue from international markets.
- Also, schemes such as duty exemption, advance authorization, duty-free import, rebate on service tax, etc. have been implemented to ease raw material imports.
- The Indian Engineering Exposition (INDEE), a brand of EEPC India, is one of the largest engineering expositions in the world.
- Apart from the specific schemes mentioned above, the Government of India has taken several initiatives to support and enhance the competitiveness of the domestic engineering goods manufacturing firms such as the “Make in India” initiative, PLI scheme for Automobile, and Auto components, PLI scheme for National Programme on Advanced chemistry cell (ACC) Battery Storage, FAME INDIA II scheme, Capital goods scheme, Industry 4.0.
- The Government of India, along with the Engineering Export Promotion Council, frequently organizes the International Engineering Sourcing Show (IESS) with the main objective of promoting India’s image and providing a platform for Indian exporters to showcase their strengths and capabilities in an emerging market. This has become a unique platform between Indian and overseas engineering firms with B2B meets, thematic seminars and exclusive country and state sessions, bilateral forums.
Also Read This: A Detailed Report On Pasta Import-Export
Government Body
- Engineering Export Promotion Council (EEPC)
Business Start Up Process
STEP 1 :- Business Registration
Proprietorship Firm
MSME (Udyam Aadhar)
Partnership Firm
Deed
ROF (Registration of Firm)
LLP (Limited Liability Partnership)
Deed
CIN (Certificate of Incorporation)
Company
MOA
AOA
ROC
STEP 2 :- PAN
Proprietor – Individual (Self)
Partnership Firm – Firm’s Name
LLP (Limited Liability Partnership) – LLP’s Name
Company – Company’s Name
STEP :- 3 GST (Goods & Services Tax)
STEP :- 4 Bank Account (Current A/c)
STEP :- 5 IEC – Importer Exporter Code
STEP :- 6 RCMC – Registration with Export Promotional Bodies (EPC, CB, DA, Etc.)
STEP :- 7 Port Registration (Nearest Port where you source)
ICEGATE Registration
STEP:- 8 COC – Chamber of Commerce
DGFT Registration
STEP: -9 Others – If Any
Documents Mandatory For Export
Pre-Shipment
a. Proforma Invoice / Agreement / Contract
b. Letter of Credit
Post-Shipment
a. Commercial Invoice
b. Packing List
c. B/L / AWB / LR
d. Certificate of Origin
e. Insurance
f. Others (if any)






